Why WaMDaM?
Currently there is no database that can organize time series, networks, scenariosand multi-attributes series, and open source for water management data

Time Series data
Flow, weather, water use
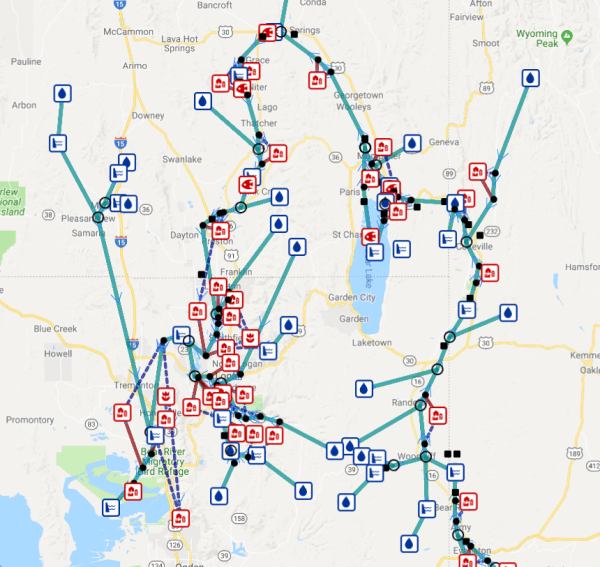
Water Networks
Track nodes and links connectivity and flow directions
Track Senarios
Version control network changes due to adding or removing infrastructure or changing data values
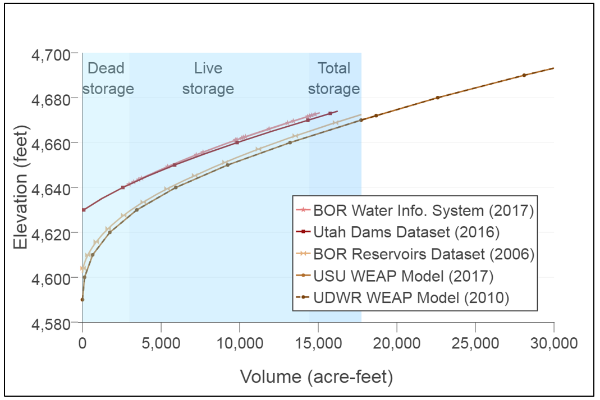
Multi-Attribute Series
Reservoir bathymetry, cost, hydropower




